Advanced Treatment Options
Minimally Invasive Gynecology Services

If you need gynecologic surgery, ask your doctor about minimally invasive options. By using robotic-assisted equipment, doctors are able to perform complex procedures with the highest surgical precision and efficiency. Many procedures that once required large incisions can now be performed with only a few tiny incisions, or no incisions at all!
Compared to traditional open surgery, minimally invasive procedures generally mean you spend less time in the hospital, have a faster recovery, less internal scarring, less pain and a lower risk of complications.
Robotic Surgery
Surgeons at the DMC use the most advanced surgical equipment, including the da Vinci® Si HD Surgical System. We were the first in southeast Michigan to have a da Vinci® Si with a dual-console configuration, making it possible for two surgeons to work on a patient at the same time.
Not only do DMC surgeons perform more da Vinci assisted gynecologic procedures than anywhere else, but our expertise is recognized on a national level and we train physicians from across the country in the use of this technology. da Vinci® Gynecologic Procedures include:
- Laparoscopic Supracervical Hysterecotomy (LSH)
- Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy (THL)
- Uterine or vaginal vault prolapse by Sacrocolpopexy
- Myomectomy (fibroid removal)
- Salpingo-oophorectomy
- Endometriosis pelvic pain treatment
Minimally Invasive Gynecologic Procedures
Densitometry
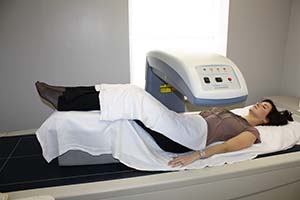
DMC Women and Infant Services offer an advanced x-ray technology called bone densitometry to identify women who are at risk of bone fractures. Bone density test equipment can help detect areas of bone demineralization before they become a serious problem, meaning you start treatment sooner and can prevent painful bone fractures or breaks. The bone densitometry technology we use is known as dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), and is the established standard for measuring bone mineral density (BMD).
The bone density test is a simple, non-invasive procedure that takes less than 30 minutes and uses extremely low-dose x-rays, much less than a standard chest x-ray.
In addition to checking for bone demineralization due to osteoporosis, the bone densitometry equipment can also detect bone loss caused by other diseases and treatments, including diabetes, cancer, lupus, kidney disease and liver disease.
The National Osteoporosis Foundation recommends bone density testing for all women over age 65. The organization also recommends bone density testing for all women under the age of 65 who have one or more risk factors for osteoporosis.
Endometrial Ablation
Ablation procedures can be very effective in controlling heavy menstrual bleeding from benign causes. By destroying the endometrial lining of the uterus, bleeding can be stopped while leaving the uterus in place, though fertility will still be lost. The physician uses a hysteroscope inserted through the vagina to destroy the endometrial lining with extreme heat, extreme cold or a special cutting device.
- Hot Water Endometrial Ablation — a minimally invasive procedure to control abnormal uterine bleeding performed in an outpatient procedure, a hysteroscope is inserted into the uterine cavity while a hot saline solution is delivered into the uterus through a tube inserted into the cervix. The water destroys the lining of the uterus in about 10 minutes. The treatment relies on the circulation of heated saline filling the uterine cavity, giving it the unique ability to treat even those women whose uterine cavities have irregular shapes.
- RF Endometrial Ablation — RF endometrial ablation is a quick, simple and safe procedure to control heavy menstrual bleeding. During this outpatient procedure, an electrode array is inserted into the uterine cavity using a hysteroscope. This electrode array gently expands to conform to the contours of each patient’s uterine cavity. After a quick test, the electrode array delivers RF energy to the uterine cavity, destroying the lining of the uterus in about 90 seconds. Most patients return to normal activities in 24 to 48 hours.
Hysterectomy
A hysterectomy is a procedure to surgically remove your uterus. There are several different types of hysterectomy:- Total hysterectomy — your surgeon removes the entire uterus and cervix, but leaves the fallopian tubes and ovaries intact. Years ago, this type of procedure was sometimes called a “partial” hysterectomy since it left the tubes and ovaries intact. Today, the removal of the fallopian tubes and ovaries is considered a separate procedure called a Bi-lateral Salpingo-Oophorectomy.
- Supracervical hysterectomy — this procedure removes the uterus but leaves the cervix intact. This procedure usually results in shorter recovery time and less pain. Most patients leave the hospital the next day and require only oral pain medications. Since it leaves the cervix intact, the procedure may result in better bowel, bladder and sexual function. This procedure is only offered to women who have no history of cervical cancer or cervical dysplasia.
Hysteroscopic Treatments
In a hysteroscopic procedure, the doctor inserts a flexible fiber-optic scope (a hysteroscope) into the uterus through the vagina and cervix. Through this approach, the physician can remove fibroids, polyps and lesions using special surgical tools fitted to the scope. Hysteroscopic procedures require no incisions.Laparoscopic Procedures
Laparoscopic procedures use a long, slender device called a laparoscope, or scope. Instead of making a large incision, the physician inserts a laparoscope through a small incision in the patient’s abdomen. The scope displays images of the internal organs on a TV monitor. While watching on the monitor, the physician inserts surgical instruments through other small incisions. Compared to open surgery, patients who have laparoscopic surgery generally spend less time in the hospital; have a faster recovery; less internal scarring; less pain; and a lower risk of complications.Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
Three small incisions are made in the abdomen. A laparoscope, a long, slender device commonly called a scope, is inserted through an incision near the belly button. The scope displays images of the internal organs on a TV monitor. While watching on the monitor, the physician inserts surgical instruments through small incisions along the patient’s waistline. A special instrument is used to cut the uterus apart and remove it in pieces through the small incisions.Laparoscopic Supracervical Hysterectomy (LSH)
This procedure removes the uterus but leaves the cervix intact. This procedure usually results in shorter recovery time and less pain. Most patients leave the hospital the next day and require only oral pain medications. Since it leaves the cervix intact, the procedure may result in better bowel, bladder and sexual function. This procedure is only offered to women who have no history of cervical cancer or cervical dysplasiaLaparoscopic Tubal Ligation/Occlusion
In tubal ligation procedures, commonly known as “having your tubes tied”, the fallopian tubes are occluded (blocked) to prevent sperm from fertilizing an egg. The procedure is commonly referred to as “tubal ligation,” but the medical term “tubal occlusion” is actually more accurate since the tubes are generally occluded (or blocked), not cut. In most cases, tubal ligation/occlusion is performed with a minimally invasive laparoscopic procedure. Recovery time for a minimally invasive laparoscopic tubal ligation is about one week or less.Myomectomy
A surgical procedure that removes fibroids but leaves the uterus intact, in a hysteroscopic myomectomy your physician inserts a flexible fiber-optic scope (hysteroscope) into the uterus through the vagina and cervix and removes the fibroids using special surgical tools fitted to the scope.In a laparoscopic myomectomy, small incisions are made so a probe with a tiny camera and surgical instruments can be inserted into the abdominal cavity. The instruments are then used to remove fibroids on the outside of the uterus.
MyoSure™ Fibroid Removal - this incision-less procedure safely and effectively removes submucosal fibroids. MyoSure™ is an excellent option for women seeking to reduce heavy bleeding symptoms and preserve uterine form and function. MyoSure is an outpatient procedure and requires no incision. On average, a 3 cm fibroid (about the size of a grape), can be removed in approximately 10 minutes. Some women will experience mild cramping after the procedure. Your doctor may recommend an over-the counter pain reliever if cramping persists. You should be able to resume your normal activity within two days.
Versapoint™ Electrosurgery - this procedure vaporizes fibroids instead of shaving or cutting them. The Versapoint™ System makes it easier for the surgeon to remove the fibroid because there are no tissue pieces left in the uterus that must be withdrawn during the procedure. The procedure is performed during an outpatient visit and offers the patient a choice of local instead of general anesthesia. A hospital stay is usually not required and patients usually return to normal activity within a few days.
Sacrocolpopexy
This is the common procedure used to repair pelvic organ prolapse. There are different types of sacrocolpopexy, including traditional and minimally invasive surgical approaches.
Salpingo-oophorectomy
This is a procedure to remove your ovaries and fallopian tubes. It can be done at the same time as other surgeries, specifically other hysterectomy procedures.
Uterine Artery Embolization
Also known as uterine fibroid embolization, this minimally invasive procedure blocks the arteries that supply blood to uterine fibroids. Using a catheter, small particles are injected into the uterine arteries. The particles block the arteries that feed the fibroids and cause the fibroids to shrink. It can be an alternative to hysterectomy.
Uterine Balloon Therapy
Designed for women who do not have cancer, a balloon is inserted through the vagina and used to remove the endometrial lining of the uterus. This procedure can be an alternative to hysterectomy.
Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE)
Uterine fibroid tumors can cause back pain, excessive bleeding, pelvic discomfort, pressure on other organs, infertility and urinary complications. Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE) is a minimally invasive treatment for benign tumors. For many women, it is an excellent alternative to a hysterectomy or open abdominal surgery, and usually reduces symptoms caused by the fibroids. UFE is a non-surgical approach to the treatment of uterine fibroids. Using imaging technology, a microcatheter will be used to insert small clotting agents that will be used to block the flow of blood to the uterine arteries - the blood supply to the problem fibroids.


